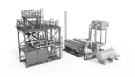
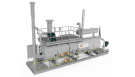
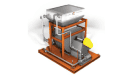
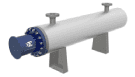
What Is Industrial Process Heating?
Industrial process heating allows companies to use thermal energy to assist with manufacturing processes or treatment of various materials and products. For example, thermal energy may be introduced to help fabricate, modify, or enhance the properties of steel, plastic, glass, cement, composites, textiles, and chemical products used in industrial processes.
Nearly three-quarters of energy across the globe is used by industrial applications. The majority of manufacturers use industrial process heating of some kind in their operations, including indirect heating to hold stable temperatures within a facility or direct heating for drying applications.
Types of Process Heating Solutions
The right process heating solution for your business will be based on the materials you want to heat and your heat source’s location. Several heating solutions are available to fit your specific needs.
Types of Fuel Sources for Industrial Heating Solutions
Industrial processing uses four main heat sources:
-
Fossil Fuels
Industrial heating solutions that utilize fossil fuel-based sources produce heat energy through combustion. The ignition of solids, liquids, and gasses allows systems like ovens, furnaces, kilns, infrared heaters, smelters, and high-temp generators to produce indirect or direct heating using radiant heat transfer or convection, respectively. Fuel options include coal, oil, or gas that produces heat energy when burned. Indirect heating systems will use a combination of burner tubes and exhaust systems that ensure the fuel source doesn’t come into contact with process materials while allowing the heat to transfer through the tube to heat the material within it, similar to the workings of a water heater.
-
Biomass
Industrial heating solutions may also use biomass, which is the most extensive type of non-fossil bioenergy source. Given their similarity to fossil fuels, which already have widespread uses for energy, biomass fuels are likewise suitable for the majority of industrial heating applications. Biomass produces bioenergy using many types of feedstock, including agricultural or wood waste material, as well as options for feedstock conversion pathways to generate process heat. Outside of direct combustion, there are also such pre-processing methods as liquefaction, torrefaction, and gasification.
-
Electricity
Some industrial process heating solutions use electricity as fuel. Direct heating systems that use this fuel source tend to transfer electricity into workpieces and materials, while indirect systems use methods such as convection, conduction, and radiation. Induction heating systems, infrared ovens, and electric arc or vacuum furnaces typically use electric-based heat energy.
-
Hybrid
Hybrid industrial heating systems may use a combination of fuel sources, technologies, and heating approaches to produce the ideal energy level and increase cost-effectiveness. For example, electric and fuel-based systems can help reduce energy expenses because of their controlled usage of electricity, with a system’s boiler running on electric energy only at non-peak times when it’s cheaper. Hybrid systems may also use a combination of convection and electromagnetic heat to optimize the direct heating processes that industries use for drying.
Environments ranging from manufacturing facilities to those involved in heavy industry require reliable process heating systems to effectively maintain stability in controlling both temperature and processes for fluids like gasses and liquids. At Sigma Thermal Inc., our process heating systems can help your application benefit from improved efficiency as well as facility, equipment, and worker safety. Our high-quality process heating solutions use varying heat sources, giving our extensive product line the ability to meet diverse process heating needs.
Process Heating Applications
No manufacturing element utilizes direct energy more than process heating, with many industries and applications using these systems. Process heating is applicable for:
- Appliances
- Electronics
- Heavy Machinery
- Paper Goods
- Food Processing
- Computer Chips
- Farming Equipment
- Textiles
- Healthcare Products
- Automotive
- Shipbuilding
- Drying Paints & Coatings
- Cosmetics
Maintenance Services
Industrial process heating allows companies to use thermal energy to assist with manufacturing processes or treatment of various materials and products. For example, thermal energy may be introduced to help fabricate, modify, or enhance the properties of steel, plastic, glass, cement, composites, textiles, and chemical products used in industrial processes.
Over time, industrial process heating systems will experience wear as components degrade via the buildup of debris or frequent contraction and expansion. Typically, immersion heaters see an output decrease of about one-third over a five-year period after initial installation. To help offset degradation, it’s important to conduct regular inspections of heating system elements based on the manufacturer’s instructions. It’s also best to have replacement heaters available in anticipation of a future breakdown, which will help minimize the potential for costly unscheduled downtime.
Request a Quote From Sigma Thermal
Sigma Thermal aims to provide you with the right industrial heating solution for your specific application. In addition to supplying a full spectrum of direct and indirect process heaters and systems, our international team of experienced professionals also provides such comprehensive services as design, engineering, automation, service, and retrofitting. We integrate superior project execution and engineering expertise with the customer support you need.
Contact us to learn more about our industrial process heating products and the Sigma Thermal difference, or request a quote today to start your project.
Contact Us Request a QuoteOur Blog
Understanding Thermal Fluids & Thermal Fluid Systems
Thermal Fluid Management • Advantages of Thermal Oil Heating Systems Types of Thermal Fluid Heaters • Work With Sigma Thermal The demand for process...
READ MOREEssential Components of Pre-Engineered Thermal Fluid Systems
As closed-loop systems, pre-engineered thermal fluid systems provide a source of heat for various industrial processes. They achieve effective and efficient heat transfer through...
READ MORE