Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Systems
What Are Waste Heat Recovery Units?
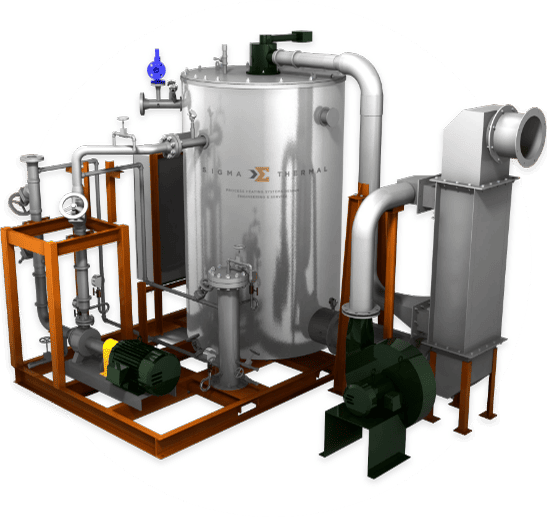
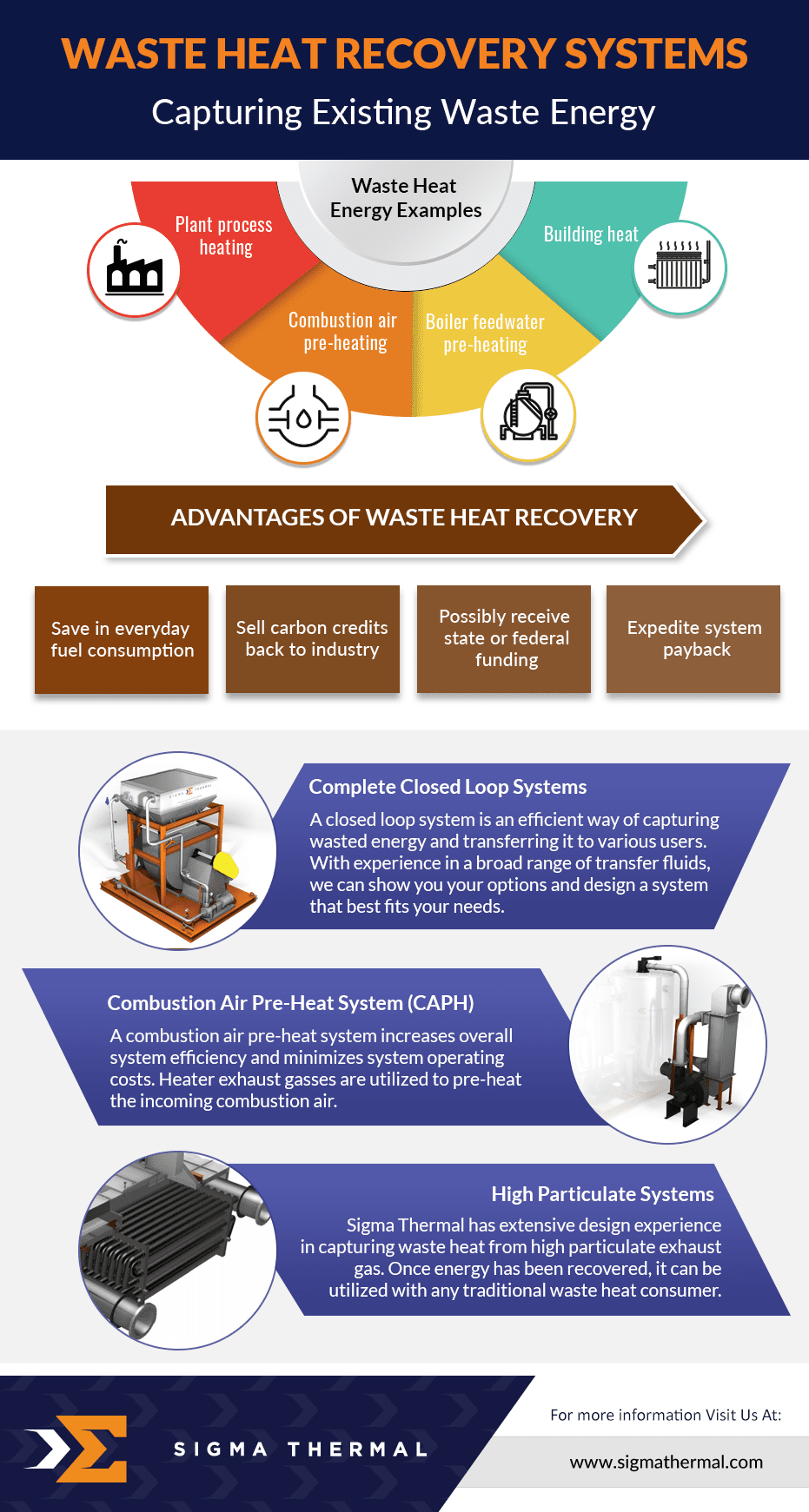
Waste Heat Recovery Units (WHRUs) work by recovering the thermal energy from the hot exhaust and gases discharged by industrial equipment such as incinerators and turbines. This energy is then repurposed to heat other media and materials, including asphalt and oil. WHRUs are available in various designs and styles.
By capturing heat that would otherwise go to waste, WHRUs allow facilities to use that energy for other applications, making them a valuable addition to various industries. They can greatly improve the overall efficiency of industrial plants.
Why Use Industrial Waste Heat Recovery Systems?
Using heat exchanger systems for industrial waste heat recovery is a simple method to enhance facility efficiency. With vast expertise in this field, Sigma Thermal collaborates with clients from diverse industries to develop innovative, profitable waste heat recovery solutions.
In addition to repurposing high-temperature waste streams, our solutions can recover and reuse low-temperature heat using heat pumps. This technology is used in heat recovery from wastewater, seawater, and data centers, where surplus heat is utilized for district heating.
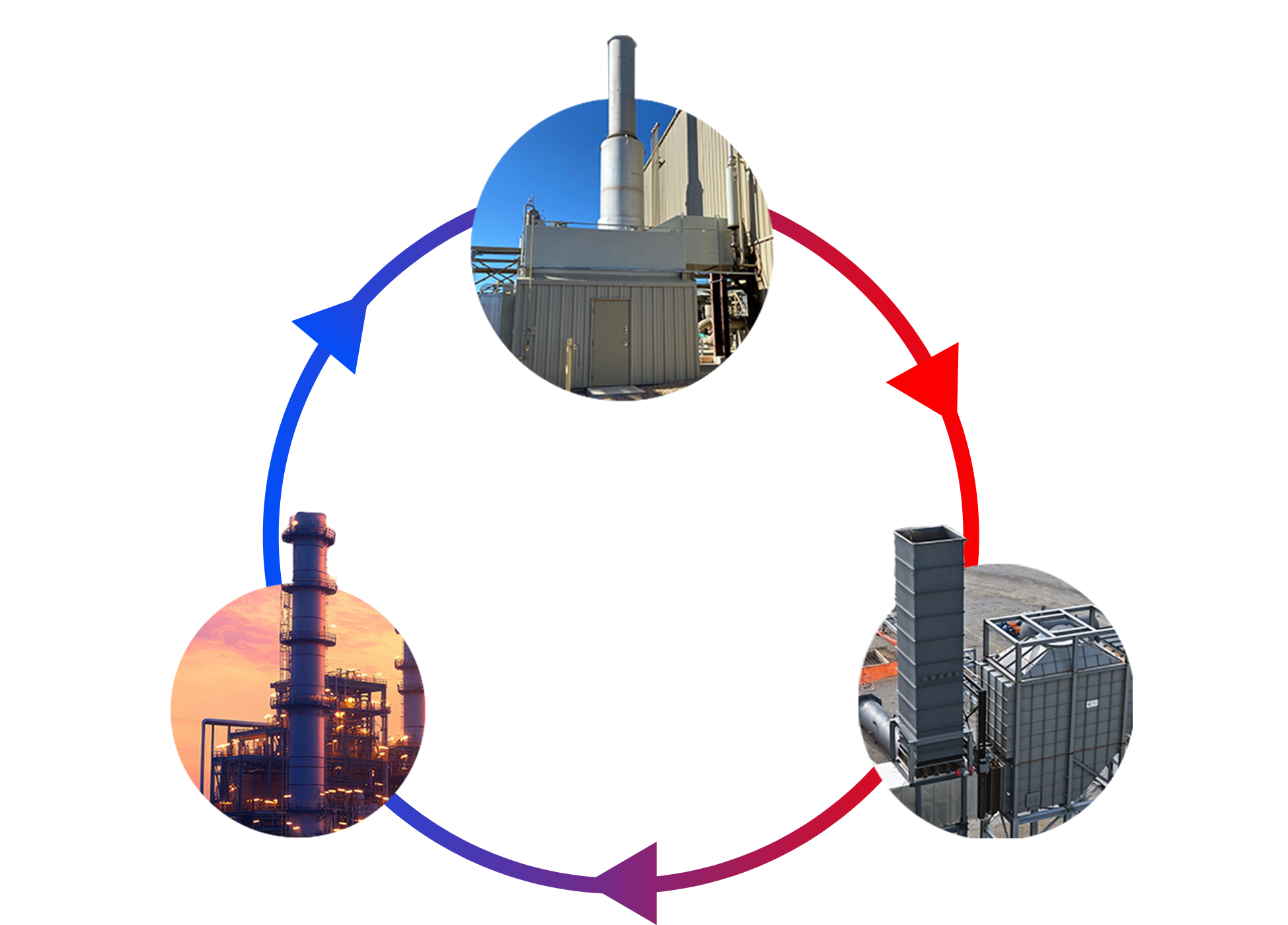
The Waste Heat Recovery Cycle Explained
A waste heat recovery cycle is a sustainable and cost-effective way to reuse thermal energy from the exhaust gas of industrial plants. It utilizes an intermediate fluid, such as oil or pressurized steam or water, to transfer heat from the exhaust gas to the organic fluid in the ORC (Organic Rankine Cycle) evaporator. The organic fluid vaporizes, expanding and generating high-pressure steam that drives the turbine. The turbine, in turn, powers the generator, producing electricity that can be utilized in the plant.
After completing its work in the turbine, the vaporized organic fluid goes through the cycle again. It moves to the condenser, where it’s cooled and turned back into a liquid before passing through the pump and beginning the cycle once more. This process enables plants to reuse the waste heat that would otherwise be lost and convert it into useful energy, reducing overall energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.